Magnesium Sulfate Treatment
Magnesium Sulfate in Pregnancy
Pregnancy complications like preeclampsia can sometimes threaten a mother’s wellbeing. It can bring on dangerously high blood pressure that increases her risk for seizures or premature birth. Magnesium sulfate treatment can address these birth injury risk factors, protecting both the mother and her baby from devastating injuries.

Magnesium sulfate can protect a mother from developing eclampsia and can prevent brain damage at birth for a preterm infant. Delaying labor contractions for even 24-48 hours can allow critical time for lung maturation and improved cerebral blood flow. This lowers a premature baby’s risk for low birth weight, respiratory distress, and brain injuries like hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy (HIE).
It is crucial that healthcare providers closely monitor the mother as she receives magnesium sulfate. Negligence when administering the medication, such as giving the wrong dosage, can cause severe birth complications. Negative effects of magnesium sulfate misuse can include magnesium toxicity, respiratory depression, cardiac arrhythmias, or even maternal mortality and stillbirth.
When a medical professional’s failure to properly administer or monitor magnesium sulfate causes injuries, legal action may be an option. An experienced birth injury attorney can investigate the facts and determine when medical malpractice occurred.
Birth Injury Malpractice Attorneys
Our birth injury lawyers help families seek justice and compensation for preventable injuries to mothers or their babies during childbirth. If you or your baby suffered preventable harm from an avoidable preterm birth, don’t hesitate to contact our firm. We can answer difficult legal and medical questions and investigate the facts on your behalf.
Free Legal Consultation
Birth Injury Lawyers
(888) 987-0005Our Birth Injury Lawyers are available to meet you in your home or the hospital.
Our vast network of medical experts and in-house nursing staff and nurse-attorneys gives us the edge over our competition. When we take your case, we assign you with not just an attorney but an entire medical team. This team includes attorneys, experienced nursing advocates, and seasoned medical experts.
Your team is available to assist with any day-to-day treatment you or your child may need. This includes assistance with obtaining medical records, scheduling doctors’ appointments, providing transportation, and any other problems that may arise.
We offer all of this on a contingency fee basis. This means you will not pay any fees until after we win your case and secure a settlement. We have an unmatched track record of birth injury results that sets us apart from other birth injury law firms.
Recent Birth Injury Settlement:
Birth Injury settlement against a hospital in which nurses and physicians failed to properly monitor the mother's blood pressure during delivery causing an HIE event resulting in neonatal seizures and cerebral palsy at birth. Our team of top-rated birth injury lawyers recovered $13,750,000 for the family to help with future medical expenses and developmental therapy.
What is Magnesium Sulfate?

Magnesium sulfate is an inorganic salt containing magnesium, sulfur, and oxygen. When used for medicinal purposes, it can come in the form of a tablet, pill capsule, liquid solution, or injection. Doctors use magnesium for a wide range of different reasons, including:
- Anticonvulsant: Seizure prevention
- Cardiovascular Medication/a>: Heart arrhythmia treatments
- Calcium channel blocker: Used to lower blood pressure
- Anesthetic: Sensory response suppressant
- Tocolytic agent: Muscle contraction inhibitor
- Anti-arrhythmia drug: Prevention of irregular heart beat
- Analgesic: Anti-inflammatory
Magnesium sulfate can also treat minor issues like constipation or muscle aches. Many pharmaceutical stores offer over-the-counter variants of magnesium sulfate to treat these ailments. However, more powerful dosages like an injection or anticonvulsant will typically require a doctor’s prescription.
What Does Magnesium Sulfate Do in Pregnancy?

Medical professionals may give magnesium sulfate to an expecting mother for a variety of purposes. These include preventing seizures from severe preeclampsia, stalling preterm labor contractions, and reducing the baby's risk of brain damage.
Premature babies have a high risk for hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy, periventricular leukomalacia, cerebral palsy, and seizure disorders like epilepsy. One study suggests that at-risk infants who receive magnesium sulfate in utero are 32% less likely to develop cerebral palsy. The same study found that magnesium sulfate reduced severe motor impairments in 39% of test cases.
What Is the Proper Dosage of Magnesium Sulfate?

Doctors give magnesium sulfate to the mother through an IV at an initial dose of 4 to 6 grams. They will pump this dosage into her system over a span of 15 to 30 minutes. They may administer “maintenance doses” at 2 to 3 grams every hour but for no longer than 7 days.
The medication typically takes effect immediately. Doctors may continue to provide magnesium sulfate to the mother until about 24 hours after she delivers her baby.
Regardless of the purpose for using it, expecting mothers who receive magnesium sulfate require hospitalization. A mother’s medical team must take careful observations of her status to monitor the medication’s effects.
What Does Magnesium Sulfate Do in Pregnancy?
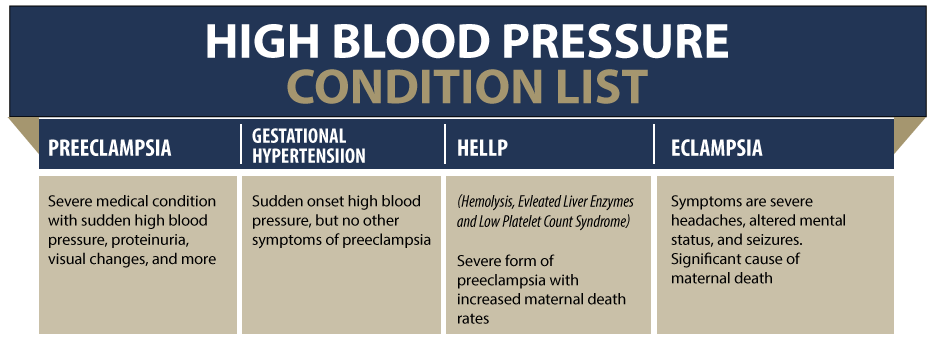
Preeclampsia is a pregnancy complication that causes high blood pressure and kidney/liver dysfunction. Most cases start after the 34th week of pregnancy, but it can occur any time after 20 weeks gestation.
The common signs and symptoms of preeclampsia include:
- Excess protein in the urine
- Intense headaches
- Nausea or vomiting
- Vision problems
- Pain in the upper abdomen, shoulders, or lower back
- Swelling or sudden weight gain, typically in the hands or feet
- Difficulty breathing due to buildup of fluid in the lungs
Preeclampsia poses the risk of birth injuries for both the mother and her unborn child. When left untreated, it can progress to eclampsia which causes neurological complications, seizures, coma, and even maternal mortality.
Magnesium sulfate can decrease the risk of preeclamptic seizures and prolong a mother’s pregnancy for up to two days. With preeclampsia, prolonging pregnancy with magnesium sulfate can give the baby additional time to develop and mature before delivery.
Allowing for additional time for the fetus to develop reduces the risk of complications associated with premature birth. While it doesn’t guarantee complications won’t happen, it ensures a stronger defense against common birth injury risk factors.
Magnesium Sulfate Treatment for Premature Birth
Preterm labor occurs when the uterus muscles start contracting early, resulting in the cervix opening before the mother’s due date. Babies born before 37 weeks gestation have a higher risk for birth injuries like hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy and cerebral palsy. This is due to their underdeveloped organs and general fragility.
Magnesium sulfate treatment can prevent or delay premature birth when a mother has an increased risk of early delivery. The medication works as a tocolytic agent to suppress uterine contractions. It does this by reducing the calcium levels, which the uterine muscles need to contract.
It is important to remember that magnesium sulfate cannot prevent labor from happening altogether. The medication can only stall it for a few days. But this delay gives medical professionals a crucial window of opportunity to administer additional medications to speed up fetal development.
Antenatal corticosteroids like betamethasone can help accelerate the development of the baby's lungs, preparing them for life outside the uterus. Betamethasone also acts as a neuroprotector, reducing the risk of brain damage and other long-term neurological complications in preterm babies.
How Does Magnesium Sulfate Protect an Infant's Brain?
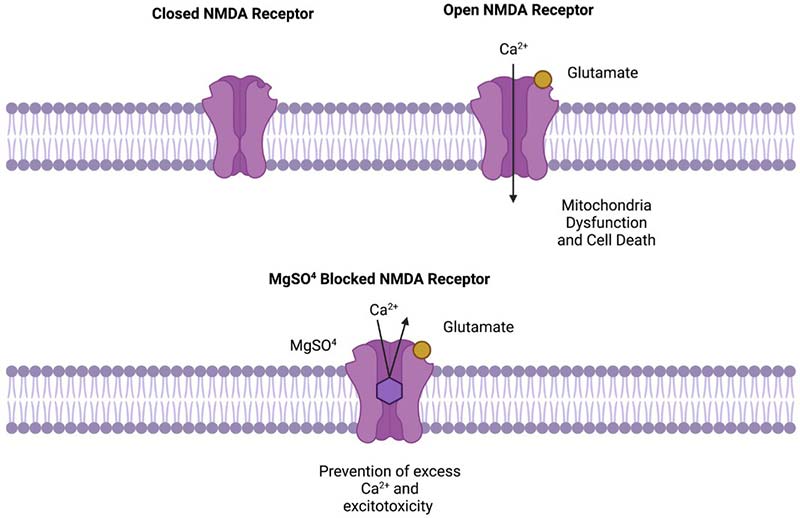
The exact mechanisms by which magnesium sulfate protects a preterm baby remain a matter of study. However, professionals hypothesize that proper and timely administration of magnesium salt promote blood flow in the brain tissues. They believe this process (known as hemodynamic stability) prevents nerve cell damage within the brain (neuronal excitotoxicity injury).
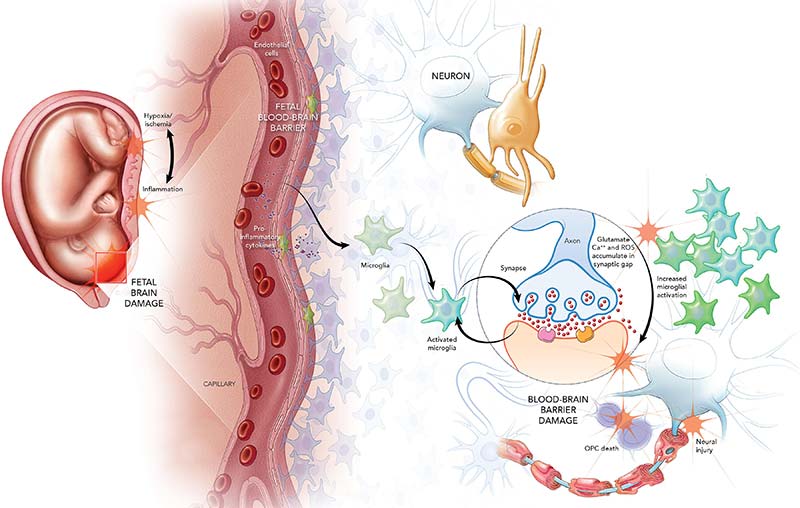
In-utero administration of magnesium sulfate may also provide the following benefits:
- Protects brain tissue from neural injury with natural anti-inflammatory and anti-oxidative properties
- Controls blood pressure and improve cerebral blood flow
- Stabilizes neuronal membranes
- Reduces excitotoxicity (A condition in which nerve cells are damaged due to overactive neural receptors)
- Mitigates the risk of oxidative injury by protecting the brain cells
- Decreases the level of inflammatory or antioxidant molecules in the brain
Doctors reduce the incidence and severity of injuries like hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy with neuroprotective agents like magnesium sulfate. Magnesium sulfate can also reduce the risk of periventricular leukomalacia and intraventricular hemorrhage, two brain injuries that are less common. Protection against these injuries greatly reduces the risk of developing cerebral palsy later in childhood.
What Are Side Effects of Magnesium Sulfate in Pregnancy?

Although magnesium sulfate can be effective for treating preterm birth and preeclampsia, it’s essential to consider the possible side effects.
For example, taking too much magnesium (magnesium overdose) can be life-threatening for both the mother and her newborn. When the mother’s body absorbs too much magnesium, she may experience lethargy and have an irregular heartbeat. She may not be able to completely empty her bladder.
For infants, magnesium toxicity can cause poor muscle control, lower bone density, and a higher risk for fractures during birth.
Other common maternal side effects of magnesium sulfate include:
- Sweating
- Nausea or vomiting
- Large drops in blood pressure
- Slow or irregular heart rate
- Muscle weakness and loss of reflexes
- Excessive sleeping (hypersomnolence)
- Respiratory arrest (loss of breathing)
- Deficiencies in minerals other than magnesium, like calcium
- Confusion or fogginess
- Coma
- Heart attack
- Chest tightness
- Changes in vision or blurred vision
- Kidney damage
- Dry mouth
Severe side effects of magnesium sulfate are rare when physicians are knowledgeable and exercise caution when prescribing and administering it. Adverse effects happen when medical professionals are unfamiliar with safe dose ranges or inadequately monitor the mother’s reaction.
Failing to properly prescribe or administer magnesium sulfate is medical malpractice when it causes otherwise avoidable injuries. It is also medical malpractice when medical professionals don’t monitor the medication’s side effects and fail to intervene in time.
Who Should Receive Magnesium Sulfate Treatment?

Physicians should administer magnesium sulfate to expecting mothers who are at risk of imminent preterm labor. Medical professionals should administer a 1-gram dose every hour until the baby arrives.
Doctors should also consider magnesium sulfate therapy as a preventative measure against seizures in mothers with severe preeclampsia.
One of the standard treatments for preeclampsia is to move along with delivery of baby and placenta. Magnesium sulfate can make early delivery safer in cases where a preeclamptic mother hasn’t fully carried her baby to term. The medication speeds up the baby's lung development and protects them against serious complications associated with premature birth.
A mother suffering from preterm premature rupture of membranes (PPROM) can also prolong her delivery with magnesium sulfate.
When to Avoid Magnesium Sulfate Treatment
In most cases, magnesium sulfate administration is fully safe. In some circumstances, however, the mother may have underlying conditions that can make the medication too risky.
Doctors should never administer magnesium sulfate to a mother with any of the following conditions:
- Muscular Dystrophy
- Myasthenia Gravis (a neuromuscular disorder)
- Compromised heart function or cardiac conduction defects
- Impaired kidney function (since the kidneys are responsible for removing magnesium from the body)
- Any other medical condition that becomes worse when taking magnesium sulfate
When monitoring for magnesium toxicity, doctors must carefully observe the mother’s urine output, deep tendon reflexes, and magnesium blood levels. Common signs of toxicity include urine output exceeding 100 mL in four hours or breathing over 12 breaths per minute.
Doctors have a responsibility to look out for common signs of magnesium toxicity to prevent the mother from experiencing complications. If they fail to watch medication’s negative effects, it can result in respiratory depression, low blood pressure, and cardiac arrest.
Do You Have a Medical Malpractice Case?

Magnesium sulfate therapy can be a beneficial treatment during high-risk pregnancies due to preeclampsia or premature birth. If a doctor does not know how to administer magnesium sulfate properly, they may make the following mistakes:
- Administering an incorrect dosage
- Ignoring or misdiagnosing signs of magnesium toxicity
- Failing to monitor the mother adequately
- Using the incorrect administration technique, such as giving doses too close together
- Failing to prescribe and administer magnesium sulfate in cases of severe preeclampsia
- Failing to prescribe and administer magnesium sulfate in cases of imminent preterm labor
If any of these mistakes lead to adverse outcomes, it may count as medical negligence or malpractice. A child can sustain permanent brain damage at birth when they do not receive medications to accelerate their development.
Families who have experienced the effects of birth injuries from medication errors deserve to know whether they were avoidable. Our birth injury lawyers help you seek justice and compensation for preventable injuries by proving medical negligence occurred. We handle medical malpractice cases involving birth injuries to babies and for mothers injured from mismanaged pregnancy complications.
What is the Statute of Limitations in a Birth Injury Case?

A statute of limitations is a law that sets a time limit on how long an injured person has to file a lawsuit after an accident.
It is essential to understand that statutes of limitations vary based on the case and the state where you file. For instance, the deadline for birth injury claims is typically different from other claims, such as injury to private property.
Generally, the clock starts ticking on the date the injury occurred. However, there are exceptions to this rule. In some cases, the statute of limitations starts when a person discovers or reasonably should have discovered an injury. When dealing with government agencies, SOLs can become even more complex.
For example, if the party that injured you was:
- A federal employee
- Employed by a military hospital, Veterans Administration facility, or a federally funded medical entity
You may need to file a birth injury claim under the Federal Tort Claims Act (FTCA). In FTCA cases, claimants must go through certain administrative procedures before filing a lawsuit. In some states, you may have less time to give notice if:
- The negligent party was a local or state government hospital
- The doctors and medical providers are employees of a governmental entity
If you file your case outside of the statute of limitations, the court will typically dismiss it. This means you will not be eligible to recover compensation for you or your child’s injuries.
Determining when a statute of limitations begins on your case can be tricky. Our birth injury lawyers can help inform you of all the important filing cutoff dates in your state. We will help your family seek justice and compensation for preventable injuries to you or your baby.
How Can Our Birth Injury Attorneys Help?

Physicians have a duty to thoroughly understand the proper administration of magnesium sulfate. This includes knowing the appropriate dosage, understanding the potential side effects, and the risks involved.
Our birth injury lawyers can identify medical malpractice and help you secure compensation to afford your child’s medical expenses. However, it first takes an expert review of the facts to determine whether medical professionals made preventable errors.
Our Process
Our team of committed attorneys, nurses and paraprofessionals works to answer these questions and seek compensation. We use our detailed medical negligence case review process to assess your potential birth injury case.
We start by learning more about your pregnancy by gathering records to determine what happened before and during your delivery. This includes evaluating prenatal testing procedures and any preventative action taken to prevent preterm birth.
We will call in skilled medical experts who review your records and provide insight into where medical professionals went wrong. If we feel medical negligence caused your baby’s injuries from premature birth, we contact you to discuss further. We will help your family seek justice and compensation for preventable injuries by proving medical negligence occurred.
At no point in our legal intake process will we ask you to pay anything. The medical review of your case and the consultation are free. We only receive payment once you do. The sooner you reach out, the sooner we can investigate your case and gather the evidence to support your claim.
We work on a contingency fee basis, meaning you will not pay any legal fees until we win your case. We do not purse any medical malpractice cases unless we fully believe we can win.
Contact us today to schedule your free consultation by calling our toll-free line at (888) 987-0005. You can also reach us by filling out our online request form.
Miller Weisbrod Olesky
At Miller Weisbrod Olesky, the attorneys, nurses, and staff understand that parents of children with birth injuries feel overwhelmed. So, every client has the attention and support of a team of trained, compassionate professionals. But we don’t just offer compassion.
We offer a process to help you discover whether your child’s birth injury, HIE, cerebral palsy or brain injury was caused by a medical error.
Call our offices today at 888.987.0005 for experienced assistance in a free consultation.
Quick Links
Testimonials
- Lyric C. I feel like our voice was heard in a sense of what can possibly go wrong in a delivery and finding us answers. I feel with our settlement, we are now in a comfortable position to provide for our son.
- Lyssa L. They are not just people that say “hey let's get you money and let's go” The law firm was very thorough with us. It was awesome. I don't want to cry, because I think about and it's amazing that they were able to help me and that we were able to help my son and get the story out there.
- Jay C. Throughout the process, one thing was clear to us, the ultimate interest of our child was the utmost concern of Max and his team and as parents navigating a situation like that, that was refreshing to know we had them firmly on our side. I highly recommend them.
