Betamethasone Pregnancy
Betamethasone During Pregnancy
A mother’s premature birth can come with several long-term health risks for her baby. For this reason, doctors will sometimes administer certain medications to advance fetal development. Betamethasone is a kind of medication doctors may consider prescribing when they suspect the baby’s organs will be underdeveloped.

When doctors fail to prescribe Betamethasone or other corticosteroids, the premature child faces multiple different risks at birth. Their underdeveloped lungs will lack sufficient levels of surfactant, a substance that helps the lungs expand and contract properly. This increases the chances of the child developing respiratory distress syndrome and requiring neonatal resuscitation or assisted ventilation.
Additionally, premature babies often are born with underdeveloped brains, increasing their risk for brain injuries like hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy (HIE). This type of brain damage at birth often comes with permanent disabilities later in life, most commonly cerebral palsy.
According to researchers, premature babies account for anywhere between 33% and 50% of all cases of cerebral palsy.
Birth Injury Medical Malpractice Attorneys
OB-GYNs, maternal fetal medicine specialists, nurses, midwives, and other healthcare providers have a duty to protect their patients from harm. If they fail to identify or treat a mother’s complications with a premature delivery, it can constitute medical malpractice.
Miller Weisbrod Olesky has a decades-long track record of results for families suffering from mismanaged labor and delivery complications. Our birth injury attorneys work tirelessly to ensure you and your child receive the treatment and financial resources you deserve. We do not charge you with a single fee until we win your case and secure compensation.
Birth Injury Lawyers
(888) 987-0005The birth injury attorneys at Miller Weisbrod Olesky are dedicated to providing compassionate legal support to families and their children living with a brain injury or birth injury, such as cerebral palsy.
What is Betamethasone?
Betamethasone is an antenatal corticosteroid therapy used to treat inflammation, allergic reactions, or various skin conditions. For expecting mothers, Betamethasone can reduce the risk of premature infant death and morbidity by promoting lung maturation.
Doctors often recommend steroid injections for expecting mothers with labor and delivery complications that may trigger preterm birth. Examples of these complications include preterm premature rupture of membranes (PPROM), cholestasis of pregnancy, or early preeclampsia.

What is Betamethasone Used For?
When a mother is at risk for premature delivery, doctors will sometimes prescribe tocolytic medications to delay labor contractions. Examples of these medications include magnesium sulfate treatment or indomethacin.
Betamethasone is not a tocolytic and does not delay premature delivery. Instead, it is a steroid that doctors inject to speed up the baby’s organ development and prepare them for birth. Doctors may opt to prescribe Betamethasone when it is not possible to delay delivery.
It is essential for the mother’s healthcare provider to accurately assess her specific circumstances before prescribing and administering Betamethasone. Doctors must weigh the potential benefits of preventing complications against any potential side effects or risks associated with the medication.
What Are Benefits of Betamethasone for Preterm Labor?
In preterm labor, steroids such as Betamethasone or dexamethasone can speed up a baby's lung development by increasing surfactant production.
Surfactant is a mixture of fats and proteins that the lung tissue normally produces in the third trimester. It lubricates the lungs and allows the air sacs to slide against one another without sticking when the infant breathes.
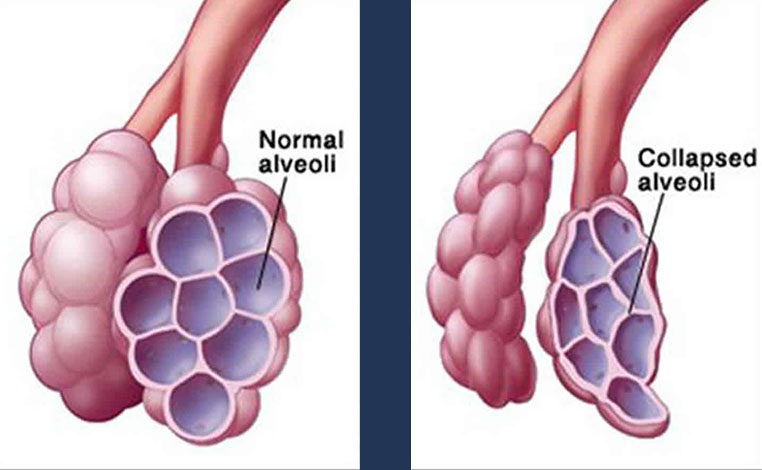
Full-term babies produce enough surfactant to breathe without assistance, but this is often not the case for premature infants. Antenatal Betamethasone can mitigate this issue by stimulating the synthesis and release of surfactant in the lungs of preterm fetuses.
The use of antenatal Betamethasone significantly reduces the risk of:
- Bleeding in the brain (intracranial hemorrhage)
- Necrotizing enterocolitis (NEC)
- Respiratory distress syndrome (RDS)
- Neonatal mortality (by about 31%)
Additionally, this medication reduces the risk of lifelong disabilities:
- Cerebral palsy (CP)
- Hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy (HIE)
- Periventricular leukomalacia (PVL)
- Delayed developmental milestones
- Neonatal seizures and epilepsy
In addition to Betamethasone, preterm babies may also require artificially produced surfactant and breathing support from a ventilator. In some cases, they may need to stay in the neonatal intensive care unit (NICU) for an extended period. In the NICU, they can receive medical care and monitoring until they are stable enough to breathe on their own.
What Risks Are Associated with Betamethasone?
Research has found that Betamethasone side effects are minimal when doctors give it late in pregnancy and in small doses. Although corticosteroids appear safe for mothers and their babies, there is always the potential for adverse reactions.
In the past, women at high risk of delivering prematurely received multiple courses of Betamethasone. However, some studies have found that more than two courses may have harmful effects, such as lower birth weights.
Corticosteroids have also been linked to adverse effects in infants, such as an increased risk of respiratory issues, infections, and neurodevelopmental disorders.
Some women with gestational or pregestational diabetes shouldn't take Betamethasone, as it can make it more difficult to control their blood sugar levels. For specific questions and concerns about Betamethasone injections used for preterm labor, consult with your primary healthcare provider.
What Other Treatments and Interventions Prevent Preterm Birth?
Aside from Betamethasone, there are other interventions that doctors may recommend to prevent complications from preterm delivery. Preventing preterm birth can significantly reduce the risk of long-term health complications for the baby. Specifically, it can lower the risk of respiratory distress syndrome, cerebral palsy, developmental delays, and vision impairments or hearing problems.
Furthermore, preventing premature delivery can reduce the risk of maternal complications, like infection, postpartum hemorrhage, and preeclampsia.
Premature Birth Interventions
Possible Doctor Treatments
A doctor might recommend the following interventions in addition to or instead of Betamethasone:
- Cervical cerclage (for women with incompetent cervix)
- Progesterone therapy
- Medications to stop contractions (Tocolytics like Nifedipine and Indomethacin)
- Antenatal magnesium sulfate (to protect the developing fetal brain)
Premature babies may stay in the neonatal intensive care unit and undergo testing to ensure their organs are maturing properly.
Some of the testing procedures in the NICU may include:
- Cardiorespiratory monitoring (keeps track of the baby's breathing and heart rate)
- Blood tests (to look for signs of certain health conditions)
- Measuring fluid input/output (tracks how much fluid the baby takes in through feeding and IV fluids and loses through diapers that are wet or soiled)
- Ultrasound (to check the brain for bleeding or fluid buildup)
- Echocardiography (to look for problems with the baby's heart function)
- Eye exam (a pediatric ophthalmologist will screen and check the baby for signs of retinopathy of prematurity (ROP))
Doctors may also administer the following treatment in the NICU to support healthy outcomes for the premature baby:
- Incubators to help control the baby's temperature and provide them with the environmental conditions they require to heal and thrive.
- Newborn G-tubes to provide fluids and nutrients to babies who are not strong enough to breastfeed or bottle feed.
- Phototherapy that reduces the amount of bilirubin in a baby's blood and treat newborn jaundice.
- Blood transfusions to treat acute blood loss before delivery or symptoms caused by anemia, such as apnea or fetal bradycardia.
- Surfactant therapy to newborns who have underdeveloped lungs and are at risk of developing respiratory distress syndrome (RDS).
- Ventilatory and respiratory support by providing a steady airflow with oxygen through ventilators or continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP).
Healthcare Provider Treatments
Healthcare providers will prescribe treatments based on the mother’s and baby's needs and an assessment of their condition. Healthcare providers are responsible for doing everything possible, including using Betamethasone as a preventative measure to prevent premature birth.
Injuries that are caused by a physician's failure to properly handle or prevent premature birth can result in long-term health complications that can place a significant financial burden on the affected individual and their families.
If you or your newborn sustained injuries due to the careless or negligent actions of a medical professional, you should consult with an experienced birth injury lawyer who can fight for the compensation you and your family deserve.
Do You Have a Medical Malpractice Case?

While medical malpractice does not cause every birth injury, an experienced birth injury attorney can help find definitive answers. For a mother whose child suffers injuries following a premature birth, medical malpractice can look like:
- Failure to identify risk factors for premature birth.
- Missing or failing to properly treat pregnancy complications that lead to premature birth.
- Failing to administer medications like Betamethasone or magnesium sulfate.
- Administering Betamethasone medications too early or too late in the mother’s pregnancy.
- Administering too high of a dosage of Betamethasone or any other type of medication.
- Delaying an emergency C-section delivery and prolonging signs of fetal distress.
- Failing to provide proper treatment after birth in the neonatal intensive care unit.
It requires a detailed review of the specific facts and timeline of events before determining whether medical malpractice occurred. Our birth injury lawyers can help seek answers to any suspicions you may have of medical errors during your pregnancy.
Statute of Limitations in a Birth Injury Lawsuit

A statute of limitations (SOL) is a law that sets a time limit on how long an injured person has to file a lawsuit after an accident. It is essential to understand that statutes of limitations vary based on the case and the state where you file. For instance, the deadline for birth injury claims is typically different from other claims, such as injury to private property.
Generally, the clock starts ticking on the date the injury occurred. However, there are exceptions to this rule. In some cases, the statute of limitations starts when a person discovers or reasonably should have discovered an injury. When dealing with government agencies, SOLs can become even more complex.
For example, if the party that injured you was:
- A federal employee
- Employed by a military hospital, Veterans Administration facility, or a federally funded medical entity
You may need to file a birth injury claim under the Federal Tort Claims Act (FTCA). In FTCA cases, claimants must go through certain administrative procedures before filing a lawsuit.
In some states, you may have less time to give notice if:
- The negligent party was a local or state government hospital.
- The doctors and medical providers are employees of a governmental entity.
If you file your case outside of the statute of limitations, the court will typically dismiss it. This means you will not be eligible to recover compensation for you or your child’s injuries. Determining when a statute of limitations begins on your case can be tricky. If you are considering pursuing compensation for a birth injury, contact an attorney as soon as possible.
How Can Our Birth Injury Attorneys Help?

Birth complications from a premature birth are not always preventable, but medical errors are. It takes an expert review of the facts of your birth to determine whether medical professionals mismanaged your delivery.
At Miller Weisbrod Olesky, our team of committed birth injury attorneys, nurses and paraprofessionals works to answer these questions and seek compensation. We use our detailed medical negligence case review process to assess your potential birth injury case.
We start by learning more about you and your child and the status of meeting/missing developmental milestones. We then gather medical records to determine what happened before, during, and after your premature birth. This includes a detailed review of the treatment doctors provided, or the treatment doctors failed to provide. Failing to administer Betamethasone can count as medical malpractice when it leads to avoidable complications in premature babies.
We will call in skilled medical experts who review your records and provide insight into where medical professionals went wrong. If we feel medical negligence caused or contributed to you or your child's injuries, we meet with you to discuss.
At no point in our legal intake process will we ask you to pay anything. The medical review of your case and the consultation are free. We only receive payment when you do. The sooner you reach out, the sooner we can investigate your case and gather the evidence to support your claim.
We work on a contingency fee basis, meaning you won't pay any legal fees unless we win your case. Contact us today to schedule your free consultation by calling our toll-free line at 888-987-0005. You can also reach us by filling out our online request form.
Miller Weisbrod Olesky
At Miller Weisbrod Olesky, the attorneys, nurses, and staff understand that parents of children with birth injuries feel overwhelmed. So, every client has the attention and support of a team of trained, compassionate professionals. But we don’t just offer compassion.
We offer a process to help you discover whether your child’s birth injury, HIE, cerebral palsy or brain injury was caused by a medical error.
Call our offices today at 888.987.0005 for experienced assistance in a free consultation.
Quick Links
Testimonials
- Lyric C. I feel like our voice was heard in a sense of what can possibly go wrong in a delivery and finding us answers. I feel with our settlement, we are now in a comfortable position to provide for our son.
- Lyssa L. They are not just people that say “hey let's get you money and let's go” The law firm was very thorough with us. It was awesome. I don't want to cry, because I think about and it's amazing that they were able to help me and that we were able to help my son and get the story out there.
- Jay C. Throughout the process, one thing was clear to us, the ultimate interest of our child was the utmost concern of Max and his team and as parents navigating a situation like that, that was refreshing to know we had them firmly on our side. I highly recommend them.