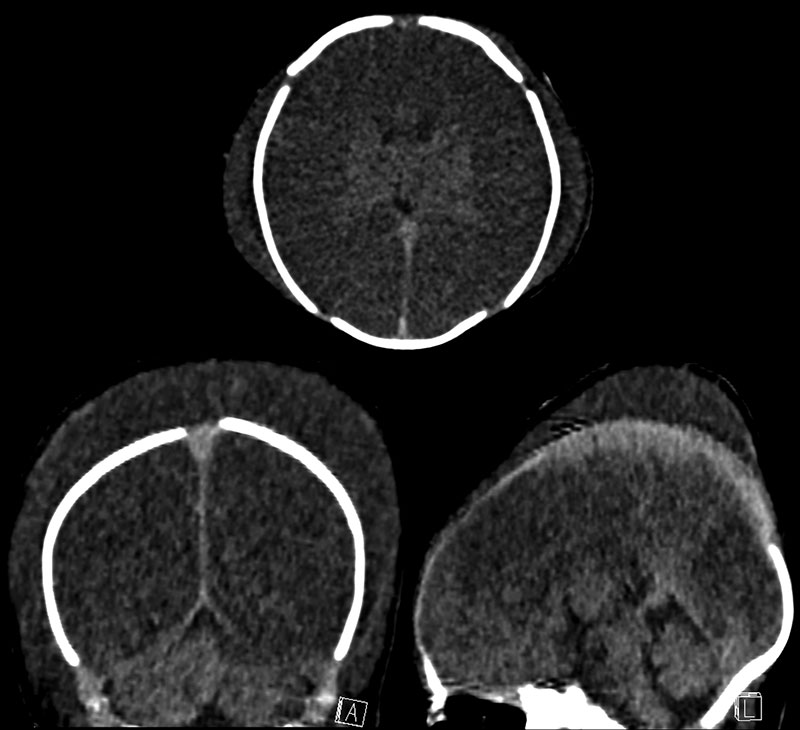
Caput Succedaneum
Newborn Caput Succedaneum
Head injuries at birth can have severe impacts on a baby’s wellbeing and their future quality of life. Injuries like caput succedaneum, however, usually present a minimal threat to the baby’s health. But when the condition is mismanaged, it can lead to other birth complications like jaundice that can cause harm.

OB-GYNs, nurses, midwives, and all other medical professionals must understand when to intervene and administer additional treatment for caput succedaneum. Negligent mistakes, like unnecessarily draining the fluid, can cause infections or other issues that will further harm the child. If a healthcare provider’s negligent mistakes lead to preventable birth injuries and complications for the baby, it may constitute medical malpractice.
Over the past three decades, the nationally recognized team of birth injury lawyers, registered nurses, and nurse-attorneys at Miller Weisbrod Olesky have established a proven track record of delivering justice for children and families across the United States who have suffered from all types of birth injuries.
Free Legal Consultation
Birth Injury Lawyers
(888) 987-0005Our Birth Injury Lawyers are available to meet you in your home or the hospital.
We are prepared to meticulously investigate the circumstances of your case, gather crucial medical records, consult with top medical experts, and fight tirelessly to secure the compensation you deserve for your child's injury.
We represent families and their birth-injured children throughout the United States. You can contact us today to schedule your free legal consultation by calling our toll-free line at (888) 987-0005 or by filling out our online request form. We work on a contingency fee basis, meaning you won't pay any legal fees unless we win your case. We only receive payment once you do.
What is Caput Succedaneum?
Caput succedaneum (pronounced kuh-PUT sec-seh-DAY-knee-um) is a neonatal head injury involving localized swelling on the newborn’s scalp (known clinically as an edema) after a vaginal delivery. The swelling comes from excess fluid made up of blood and blood serum, which is a clear, yellowish substance responsible for separating blood after it clots.
The edema is usually benign, resulting from the compression and pressure on the baby’s head as they pass through the birth canal.
What Causes Caput Succedaneum?
Caput succedaneum is most often caused by excessive pressure placed upon the baby’s head, but it can sometimes happen even before they’re born.
During gestation, the swelling may occur from the premature rupture of membranes (PROM), which is when the mother’s amniotic sac in the womb breaks early before labor. When the amniotic sac is unable to support the head of the fetus, it will allow more pressure on the head from the pelvic bones, causing the fluid to build up under the baby’s scalp.
More commonly, though, caput succedaneum is caused by a labor and delivery complication during vaginal birth.
What Causes Caput Succedaneum During Delivery?

Caput succedaneum can occur during a prolonged labor or if the baby’s head is stuck due to cephalopelvic disproportion.
Other complications that can prolong labor include macrosomia and uterine hyperstimulation, where excessive and forceful contractions can place extreme pressure on the baby’s head. The improper use of delivery instruments like forceps and vacuum extractors can also cause head swelling.
Although caput succedaneum may develop in any baby during delivery, medical providers should be alert to the following risk factors, which increase the baby’s likelihood of having it:
- Premature rupture of membranes (PROM)
- Fetal macrosomia (the baby’s head is much larger than average)
- Cephalopelvic Disproportion
- Oligohydramnios (low levels of amniotic fluid)
- Braxton Hicks contractions (false labor)
- Assisted delivery (use of vacuum extraction or forceps)
Signs and Symptoms of Caput Succedaneum
A key symptom of caput succedaneum is a soft, puffy, and swollen spot (typically 1-2 cm deep) primarily on the part of the head which first went through the birth canal. But sometimes the spot may extend to both sides of the scalp. Noticeable changes to the skin color or bruising may also be present in the affected area.
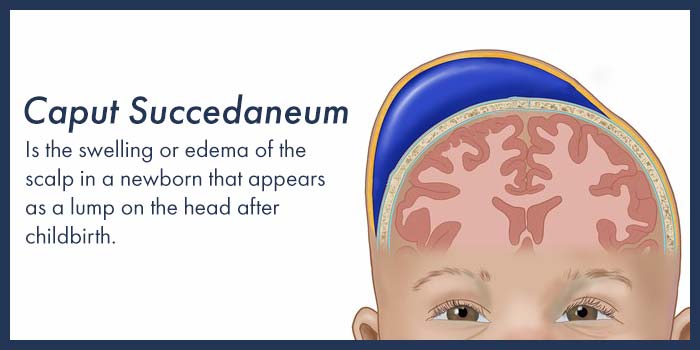
For correct diagnosis, the medical provider should be able to differentiate between the symptoms of caput succedaneum and other more serious medical conditions, such as skull fracture, brain bleeds or hydrocephalus (which also causes swelling in the baby’s head, but generally in a different area.)
The medical provider should also be mindful to distinguish caput succedaneum from newborn cephalohematoma (buildup of ruptured blood vessels in the tissue that covers the baby’s skull.) Swelling caused by caput succedaneum is subcutaneous (under the skin), while the swelling caused by cephalohematoma is within the skin tissue.
What Are Possible Complications of Caput Succedaneum?
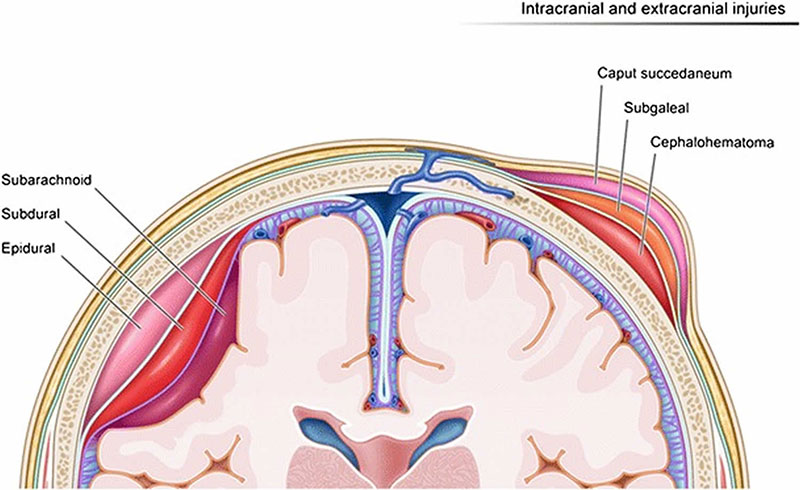
Being a relatively benign condition, caput succedaneum doesn’t carry many concerning health complications for the child in the long term. Some families have reported cases of hair loss around the area of swelling and light scarring. Sometimes, however, swelling and bruising from caput succedaneum can increase levels of bilirubin in the blood, which can result in newborn jaundice if mismanaged or left untreated.
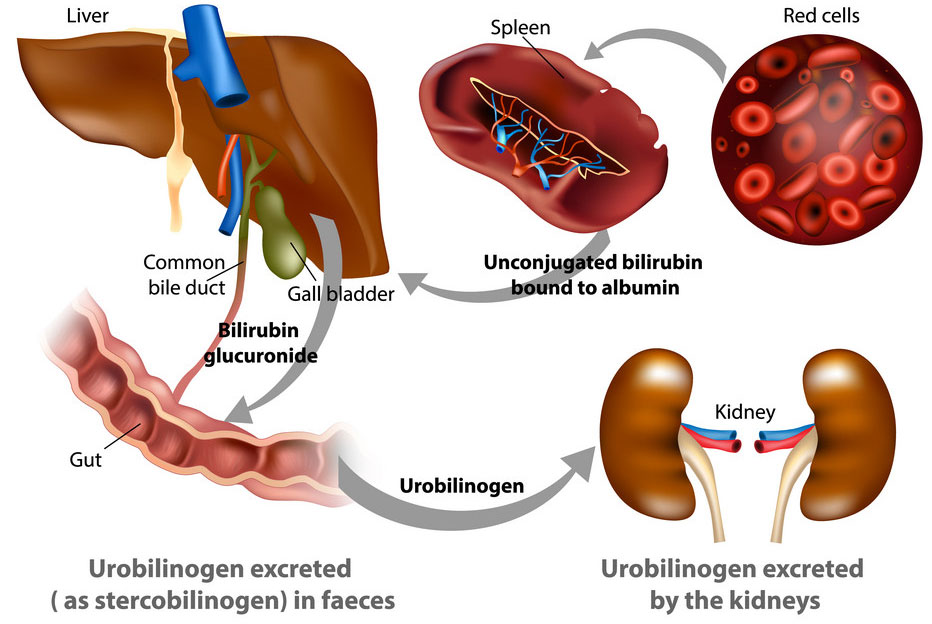
Some babies with jaundice will require further medical procedures, including a blood transfusion, phototherapy, or treatment of any underlying causes.
When newborn jaundice is not diagnosed on time or improperly treated, it may result in a serious neonatal birth complication known as kernicterus. This is a life threatening and permanent form of brain damage that occurs when excess levels of bilirubin cause toxicity in the brain tissue. Babies with kernicterus may eventually develop cerebral palsy or other lifelong disabilities.

How is Caput Succedaneum Diagnosed?
Depending on the conditions, medical providers may be able to reliably diagnose caput succedaneum as early as the first stage of labor using neuroimaging via an ultrasound of the baby’s scalp.
According to the Academy of Neonatal Nursing recommendations, medical professionals should always compare the potential symptoms of caput succedaneum with those of newborn cephalohematoma.
Making this distinction is vital because undiagnosed caput succedaneum may lead to kernicterus, while newborn cephalohematoma may lead to complications, such as anemia and blood clotting.
When medical providers fail to follow medical standards that should lead to the differentiation between caput succedaneum and cephalohematoma and a birth injury or brain injury occurs a medical malpractice lawsuit may be available for the family of the injured baby.
How Long Does Caput Succedaneum Last?
Most caput succedaneum cases will self-resolve within 48 hours. Attempting to drain the fluid from the baby’s scalp can cause neonatal infections, so it should be avoided. All babies diagnosed with the condition should also be monitored for the risk of newborn jaundice.
Failure to properly monitor and treat newborn jaundice may cause kernicterus, which is a dangerous and life-threatening birth complication. Kernicterus develops when excess levels of bilirubin invade the brain tissue, leading to permanent brain damage. Failure to diagnose and treat jaundice and kernicterus is among the most common reasons for a medical malpractice lawsuits arising during the neonatal time period.
Caput succedaneum is also a key indicator to show that the baby when through a stressful and difficult delivery, and their head was subjected to considerable external pressure at the time of birth. This should alert the medical provider to the possibility of a more serious brain injury, such as hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy (HIE) resulting from birth asphyxia, which can lead to cerebral palsy.
Is Your Child’s Birth Injury the Result of Medical Malpractice?

Parents whose children suffer from caput succedaneum related birth injuries or birth complications are entitled to answers as to the cause of their child’s injury and whether mistakes by the doctors and nurses contributed to the injury.
- Were there signs of birth injuries or birth complications during the pregnancy, labor, and delivery process, or presence of risk factors, which were either not recognized or properly treated?
- During the labor and delivery, were there clear indications that their baby was suffering from fetal distress, but appropriate actions were not taken by the obstetrician or nurses?
- Did the medical team fail to recognize a common caput succedaneum birth complication like jaundice?
- Did your baby suffer a serious brain injury as a result of kernicterus due to improper neonatal treatment?
Our birth injury attorneys have extensive experience in this and all areas of birth injury medical malpractice. The lawyers and nurses at Miller Weisbrod Olesky will help you determine if mistakes of the medical providers caused a birth injury to your child, including Hypoxic-Ischemic Encephalopathy (HIE) or cerebral palsy.
Our award-winning birth injury attorneys have represented families all over the United States in their time of need after a birth injury. We use our experience and expertise to obtain for you and your child a medical malpractice settlement that will help provide specialized medical therapy in order to maximize the quality of life and independence of your child throughout their life.
Sometimes families are reluctant to contact a medical malpractice lawyer. It’s also not uncommon for parents to feel overwhelmed by the responsibilities they encounter in caring for their injured child and worried that they will not be able to help out in a lawsuit involving their child’s birth injury. Our birth injury attorneys and nursing staff will address these hesitations and concerns, so you can focus on your child and maximizing their care.
How Can the Birth Injury Attorneys at Miller Weisbrod Olesky Help?

A child’s caput succedaneum shouldn’t cause brain damage or other severe harm to their health. But when it does, it takes a detailed expert review of the facts and circumstances of your pregnancy and birth to determine whether the injury was the result of medical malpractice.
Our Process
At Miller Weisbrod Olesky, a team of specialized birth injury attorneys, nurses and paraprofessionals uses our detailed medical negligence case review process to assess your potential birth injury case.We start by learning more about you and your child and the status of meeting/missing developmental milestones. Then we gather medical records to determine what happened before, during, and after your delivery. We call in skilled medical experts who review your records and let us know if they think medical errors could have caused you or your child's injuries.
If we feel medical negligence caused or contributed to the child’s caput succedaneum, we meet with you to discuss how you can receive compensation from the medical professionals who made the errors.
At no point in our legal intake process will we ask you to pay anything. The medical review of your case and the consultation are free. We only receive payment when you do. The sooner you reach out to us, the sooner we can begin investigating your case and gathering the evidence needed to support your claim.
We work on a contingency fee basis, meaning you won't pay any legal fees unless we win your case. Contact us today to schedule your free legal consultation by calling our toll-free line at (888) 987-0005 or by filling out our online request form.
Contact Our Birth Injury Lawyers
Miller Weisbrod Olesky
At Miller Weisbrod Olesky, the attorneys, nurses, and staff understand that parents of children with birth injuries feel overwhelmed. So, every client has the attention and support of a team of trained, compassionate professionals. But we don’t just offer compassion.
We offer a process to help you discover whether your child’s birth injury, HIE, cerebral palsy or brain injury was caused by a medical error.
Call our offices today at 888.987.0005 for experienced assistance in a free consultation.
Quick Links
Testimonials
- Lyric C. I feel like our voice was heard in a sense of what can possibly go wrong in a delivery and finding us answers. I feel with our settlement, we are now in a comfortable position to provide for our son.
- Lyssa L. They are not just people that say “hey let's get you money and let's go” The law firm was very thorough with us. It was awesome. I don't want to cry, because I think about and it's amazing that they were able to help me and that we were able to help my son and get the story out there.
- Jay C. Throughout the process, one thing was clear to us, the ultimate interest of our child was the utmost concern of Max and his team and as parents navigating a situation like that, that was refreshing to know we had them firmly on our side. I highly recommend them.